Enabling Efficient Healthcare with IoT
- According to Fortune Business Insights, the IoMT market is estimated to hit USD 142.45 billion by 2026. This growth is driven by an increase of chronic diseases and better healthcare infrastructure worldwide.
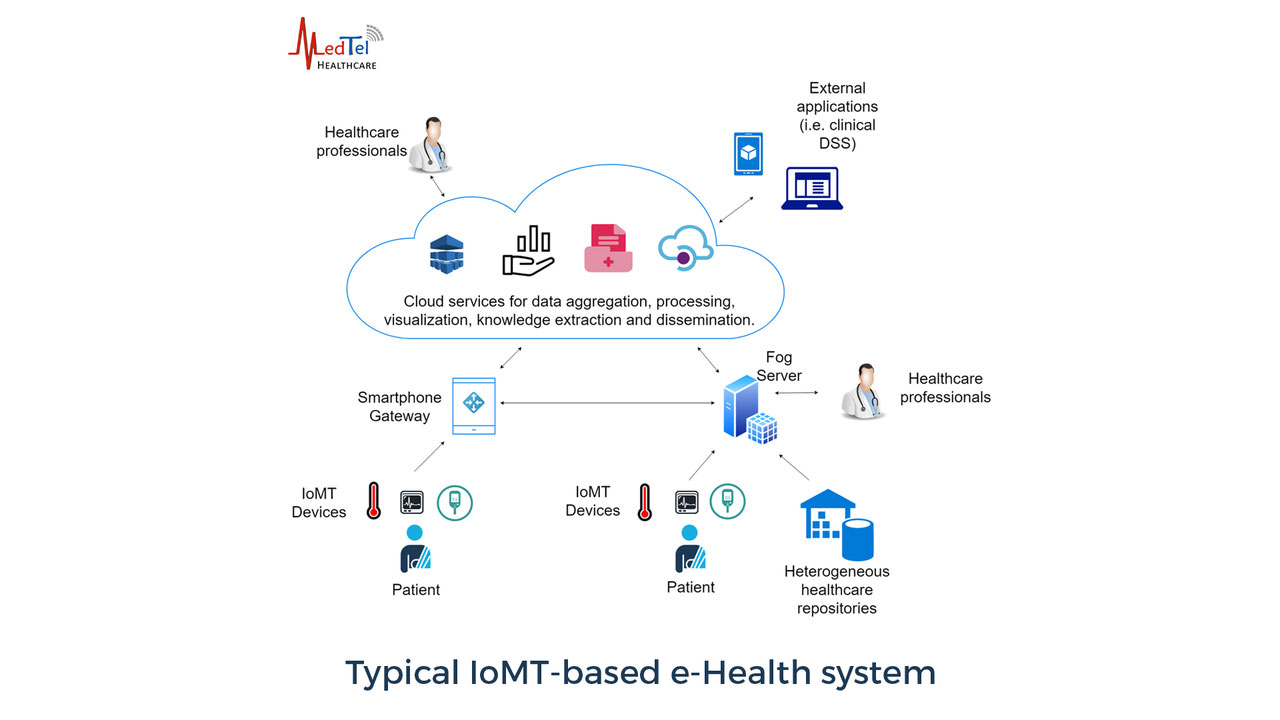
The IoMT and Connected Care Ecosystem
IoMT-based platforms can empower patients to become self-aware of their health. Oftentimes, patients can even minimize the intervention of healthcare professionals. These platforms also empower physicians by simplifying the healthcare process and supporting clinical decisions.
Factors Driving IoMT in Healthcare
- Increasing awareness of the benefits of using smart healthcare products.
- Improved efficiency of smart healthcare devices.
- Rise in R&D of advanced devices.
- Increasing disposable income of people.
Types of RPM Healthcare Devices
- electroencephalographs (EEGs)
- electronic thermometers
- electrocardiographs (ECGs)
- electronic stethoscopes
- spirometers
- cardiac monitors
- apnea monitors
- audiometers
- oximeters
- blood pressure monitors
- breathing frequency monitors.
Irrespective of what type of device/sensor is used, it must comply with medical device and medical software safety standards, must comply with data privacy and data protection laws, and be able to be integrated with a healthcare provider’s system. This ensures that IoT devices can enable proper communication between patients and healthcare providers without comprising data security.
Benefits of IoT in Healthcare
Efficient Drug Delivery
Reduced Errors
Better Patient Engagement and Experience
Lower Costs
The last few decades have seen incredible medical breakthroughs but the rising cost of treatments means that they’re out of the reach of many patients. Enter IoT and its capacity to offset costs. The adoption of wearable devices, biosensors, and connected care, reduces the need for specialists and hospital room expenses, while decreasing staffing costs, and streamlining claims processing. Using remote diagnostics technology, medical equipment manufacturers can also monitor and manage hospital equipment, which is otherwise expensive to maintain.
Challenges of IoMT
Managing IoMT Risks
- Taking a DevSecOps and security by design approach to IoMT systems.
- Using embedded software protection tools.
- Deploy only patched and monitored devices.
- Implement end-to-end security.
Future Predictions of IoT in Healthcare
IoT became (and continues to be) the way forward, offering patients and healthcare providers a simple, sustainable, and affordable solution to care. Advancements in IoT, expanded connectivity, and a greater acceptance of digital health technologies will continue to increase the adoption of IoT in healthcare.
Also Read: The Future of Digital Healthcare and Patient Monitoring